 representing the element to see that this element has order 2.
representing the element to see that this element has order 2.
Similarly you can verify that g has order 3 and h has order 2.
Composing powers of g and h gives the set: {x, 1 - x, (x - 1)/x, 1/(1 - x), 1/x, x/(x - 1) }.
This is a non-abelian group of order 6 and so is S3 .

Choose any point not on the first line l and join it to the first three points. Put in the second line m and adjust it so that two of the points are on the correct lines. Then tilt m until the third point lies on the correct line. You may have to experiment a bit to see how to do it if the points are (say) in different orders on the two lines.
In fact the converse of this result is true: any map from RP1 to RP1 given by projection from a point not on either line does give an element of PGL(2, R).
 maps the three given points to a, b and c.
maps the three given points to a, b and c.
To map [1, 1, 1] to the fourth point means solving the equations a1/α + b1/β + c1/γ = 1, etc for 1/α, 1/β and 1/γ and we can do this since the matrix of coefficients is non singular (otherwise a, b and c would be on a line).
Then, as in the case of RP1, if θ maps these four standard points to a, b, c and d and φ maps them to a', b', c' and d' then the map we need is φ  θ-1.
θ-1.
Note that |V| = |F|n and we do not use the 0 vector. So using the fact that each equivalence class has |F| - 1 elements (since λ can take any value except 0) we get |P(V)| = (|V| - 1)/(|F| - 1) as required.
To get a projective plane we need n = 3. So taking F = GF(3) gives a 13 point plane (in which each point lies on 4 lines and 4 lines pass through each point. If |F| = 4 then you get a 21 point plane.



Project P and Q to points on the line at infinity. This then gives a diagram:
Then 12 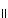 54 and 23
54 and 23 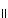 65 and we need to show that 16
65 and we need to show that 16 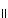 34.
34.
To show this, prove that Δ016 and Δ034 are similar.
To do this note that (by similar triangles) 01 : 05 = 02 : 04 and 03 : 05 = 02 : 06
So 01 . 04 = 02 . 05 = 03 . 06 and so 01 : 03 = 06 : 04 which is what we need.