Theorem
Closed: like [a, b]
Half-open: like [a, b), (a, b], [a, ∞), ...

| Previous page (The boundedness theorem) | Contents | Next page (Analysis Summary) |
Theorem

Closed: like [a, b]
Half-open: like [a, b), (a, b], [a, ∞), ...

For example, (-π/2, π/2)→ (-∞, ∞) by the tangent function.
(-∞, ∞)→ (0, ∞) by the exponential function.
Any finite open interval can be mapped to any other finite open interval by a suitable linear function. (Exercise)
For example, (-∞, ∞) or [0, ∞)→ [-1, 1] by the sine function.
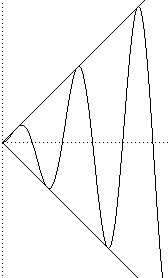
Any open interval can be mapped to a half-open interval.
For example, (-∞, ∞)→ [0, ∞) by the x2 function.
| Previous page (The boundedness theorem) | Contents | Next page (Analysis Summary) |